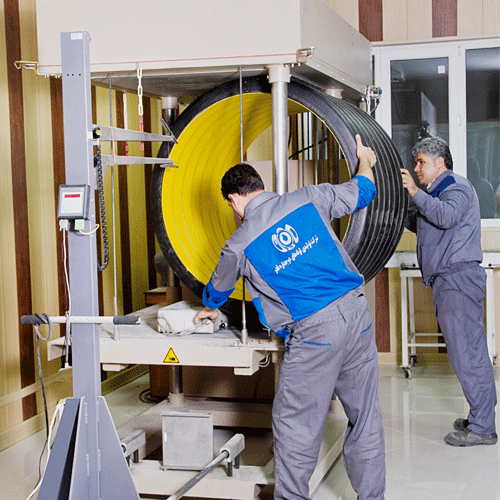
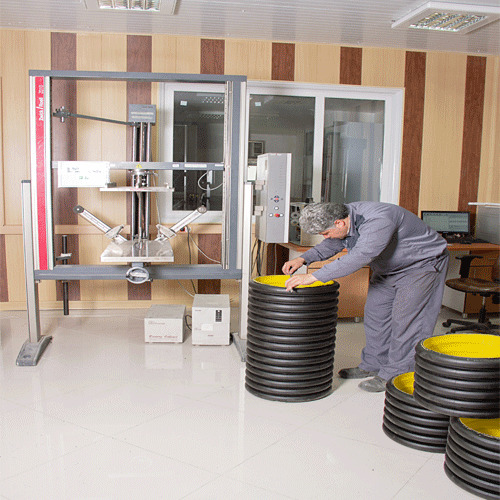
The laboratory of Ghadr Double Wall Pipes Manufacturing Company is one of the best equipped laboratories in the polyethylene pipe and fittings industry in Iran. This laboratory is equipped with modern measuring and testing devices (polyethylene pipes) and tests all products and raw materials in accordance with the standards and can be a reliable reference for quality decision making of double-walled pipes. It is noteworthy that the laboratory has a standard of 17025, which indicates the calibration of equipment and standardization of instruments, and confirms the competence of the laboratory to test products and the accuracy of the results obtained. The production of polyethylene pipe should be under the supervision of the laboratory and quality control unit so that the final pipe is of high quality and can be serviced at the project site with the highest standards in pipe production.
This laboratory has been operating in the field of testing pipes, fittings and polyethylene raw materials for about 2 decades and has the ISO / IEC 17025 laboratory quality management standard certificate from the National Certification Center of Iran.
Ghadr Company’s laboratory provides a wide range of services to domestic and foreign customers with the most accurate and advanced European equipment and capable personnel and experts in the field of polymer.
List of laboratory equipment
Row |
device name |
Type of test |
|
1 |
IPT-Germany ring stiffening machine |
Long-term, short-term cyclic stiffness and flexibility |
|
2 |
MFR device-Germany |
Melt flow index test |
|
3 |
Avon: Heraeus – Germany |
Determination of carbon dispersion samples |
|
4 |
Carbon Black-IPT device Germany |
Determine the percentage of carbon |
|
5 |
Mettler precision scales |
Weighing and determining density |
|
6 |
Zwick Ring Tightening Machine – Germany |
Long-term, short-term cyclic stiffness and flexibility |
|
7 |
German OIT-NETZSCH machine |
Determination of oxidation and thermal stability |
|
8 |
30 and 20 cm digital caliper – Mitutoyo Japan |
Dimension measurement |
|
9 |
Microscope device with analysis software |
Determine the soot distribution |
|
10 |
IPT-Germany impact machine (Falling weight) |
Perform impact test |
|
11 |
Water Tightness |
Perform a sealing test |
|
12 |
Water Jetting machine |
Perform a waterjet test |
Melt Flow Index (MFR)
This test is performed according to ISO 1133 standard. In this test, the flow rate of molten raw materials is measured at a constant temperature and time to check the results of how the materials behave inside the extruder in order to create a suitable process. This test is performed for raw materials to confirm the quality and viscosity of materials and also to check the product to control the quality of the production process and compare it with the results of raw materials, which according to the standard , Otherwise the production process will require new settings.
3 to 5 grams of the sample of pipe or raw materials are poured into the MFR device with a temperature of 190 degrees and the test time is 10 minutes. After the test, the output parts of the device are weighed. It is 10 minutes.
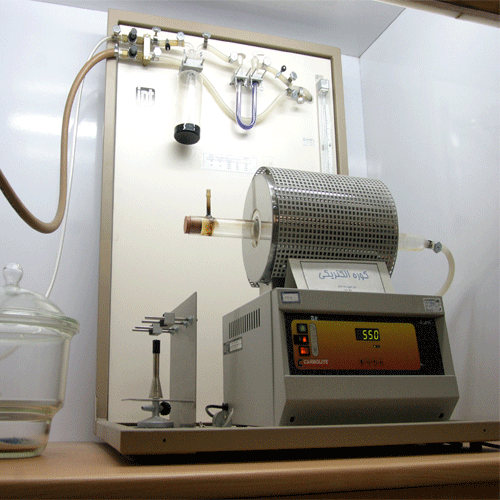
Carbon Black Content
This test is performed according to ISO 6964 standard. The purpose of this test is to calculate the percentage of carbon in the pipe, which according to the product characteristics standard should be between 2 to 2.5 percent. In order to increase the resistance of the pipe to the sun’s rays, it is necessary to add soot to the raw materials during a proper process. If the amount of soot in the final product is less than necessary, the polymer will not have sufficient resistance to sunlight. If the amount of soot is too much, the concentration of stress is created and makes the pipe brittle and the pipe becomes vulnerable.
In this test, 1 gram of sample is placed at 550 ° C for 45 minutes in the presence of pure nitrogen gas. At the end of the test, the available hydrocarbons are burned and only the amount of carbon present in the sample remains. Obtained.
Investigation of soot distribution (Carbon Black Dispersion)
This test is performed according to ISO 18553 standard. The required moisture to protect polyethylene pipes from UV rays is the appropriate amount of soot in the final product, but this amount alone is not enough. Due to their special chemical structure, soot particles tend to cluster and so-called stick together, so the masterbatch mixing process should be such that the particles, in addition to dispersion and dispersion, are properly distributed on the polyethylene surface to be effective. Optimal in full protection of polyethylene.
Recent research has shown that cracking in pressurized pipes begins at the site of soot accumulation, especially when carbon accumulation is linear; Because the accumulation of soot in the pipe acts like a foreign object in the wall of the pipe and causes failure.
Examines how carbon is distributed in the pipe. Since soot particles, due to their special chemical structure, tend to cluster and so-called stick together, so the masterbatch mixing process should be such that the particles, in addition to being crushed and dispersed evenly and evenly on the poly surface. Ethylene should be distributed so that it can have a favorable effect in the complete protection of polyethylene.
In this test, 6 samples with a weight of 0.25 05 0.05 mg were cut and prepared with the help of a sharp blade and the test samples should be separated from different parts. The samples are placed on the slide regularly and at the same distance. Another clean slide is placed on the slide and the 2 slides are connected with a tight metal clamp.
The prepared slide is placed in the oven at a temperature between 150 and 210 degrees (preferably 180 degrees) for at least 10 minutes to melt the sample and be ready to be placed under a microscope, then magnified 100 times by microscope and grid software And its rate is calculated that its rate must be less than 3.
Ring Stiffness (SN)
This test is performed according to ISO 9969 standard. To determine the short-term ring strength of corrugated pipes, 3 pipe samples with a length of 30 cm are selected and the desired force is applied to the pipe according to the formula according to the relevant standard, and the deformation of the pipe should not be more than 3% of the pipe diameter. The speed of each size is according to the table below. Each sample is tested at an angle of 0 ° 120 ° and 240 °.
Long Ring Stiffness (SR24)
This test is performed according to DIN 16961-2. To determine the long-term ring strength according to the relevant standard, a sample with a length of twice the inner diameter of the pipe and a maximum of 1 meter is selected and the sample should be placed in a laboratory at 23 2 2 ° C for 24 hours to relieve production stresses. According to the pipe series, the desired force of that series is applied to it for 24 at a temperature of 23 2 2 (usually the pipes used in the sewage collection system are 31.5 kN / m2 of series 5) and the deformation of the pipe In 1, 6 and 24 hours it should not be more than 3% of the inner diameter of the pipe.
Ring Flexibility
This test is performed according to EN 1446 standard. For this test, 3 samples of 300 mm long tubes are prepared and the samples should be placed in a laboratory environment for 24 hours at a temperature of 23 2 2 degrees to relieve production stresses.
Samples are subjected to pressure at angles of zero, 120 and 240 degrees, respectively, up to 30% of the outer diameter of the pipe. The inner layers of the outer layers are separated from each other.
Water Tightness
This test is performed according to EN 1053 standard. In this test, first, using EPDM sealing washers for each size, the pipes are connected from the coupler and spigat part and both ends of the pipe are closed using a suitable drip and water flows into the pipe and Using a suitable gauge, the water pressure inside the pipe is controlled to reach 0.5, then for 1 minute under the applied pressure, no water leakage should be observed from the coupler connection.
Impact or TIR (Falling weight)
This test is performed according to EN 744 standard. In this test, the resistance of the pipe to external shocks is measured and this test is performed at a temperature of zero degrees. % Be.
The length of the prepared sample should be 10 ± 200 mm and should be placed in a tank containing zero degree water for 1 hour before the test.
We have two types of weights, which are named d25 and d90 based on the diameter of the surface hitting the pipe
Number of lines that must be drawn longitudinally inside the pipe according to different instruments:
Number of lines |
Size (mm) |
|
6 |
110 |
|
12 |
250-200 |
|
16 |
315 |
|
24 |
400≤ |
The number of samples prepared should be such that according to the number of lines drawn in the pipe, at least 25 strokes should be applied in order to calculate the TIR.
The weights used in this test are of type d90, which are specified in the table below in terms of height and weight of the weight according to the size of the pipe:
Height (mm) |
Mass (kg) |
Size (mm) |
|
1600 |
0/5 |
110 |
|
2000 |
6/1 |
200 |
|
2000 |
2 |
250 |
|
2000 |
5/2 |
315 |
|
2000 |
2/3 |
315< |
View of the laboratory location
Water Jetting test
This test is based on the WIS 4-35-01 method. In this way, a sample of a tube with a length of 30 cm is installed in the device and the nozzle of the device is adjusted with an angle of 30 or 45 degrees and water with a pressure of 150 to 180 bar (depending on the size of each tube) and a temperature of 10 ± 15 in 5 points and Each point is applied for 120 seconds with a vertical distance of 5 cm to the inner surface of the pipe. Or a hole is made in the inner surface of the pipe.
Pipe inspection and inspection (ISO 11922)
Examining the appearance of polyethylene pipes is not only the simplest quality control test, but it is also of special importance that polyethylene pipes must be free of any imperfections (internal and external) and deep pores. Minor depressions can be ignored as long as they do not reduce the thickness to less than the allowable level.
Dimensional measurement and control (ISO 11922)
Accurate determination of pipe wall thickness is determined using calibrated calipers in the cutting section and ultrasonic thickness gauge along a pipe branch.
The outer diameter of the pipe is measured using a calibrated metal tape (cichrometer) along a branch of the pipe and its average value is reported.